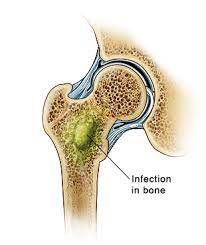
 Children can develop infections in their bones, joints, or muscles.
Children can develop infections in their bones, joints, or muscles.
Infections are usually caused by bacteria that are present in our normal living environment. The most common bacteria causing bone, joint, or muscle infections in children is Staphylococcus aureus (often referred to as “Staph” infections).
Bacteria can get into the body in a variety of ways. They circulate through the bloodstream until they reach a bone, joint, or muscle. Bacteria then leave the bloodstream and multiply in the bone, joint, or muscle tissues.
Infections pose special risks to young children for a number of reasons:
- Children under the age of three are easily infected. Their immune systems are not fully developed and they tend to fall down a lot, opening the skin to infection.
- Infections spread quickly through a young child’s circulation system and bone structure.
- Damage to bones and joints caused by infection can harm a child’s growth and lead to physical dysfunction. Infection of child’s hip joint is a surgical emergency.
Children who have infections of their bones, joints, or muscles often have the following:
- Fever
- Pain
- Limited movement of the infected area — your child may limp
- Infants may be irritable and lethargic, refuse to eat, or vomit
It is important to bring your child to a doctor immediately if symptoms are not quickly resolving at home.
Antibiotic Treatment
The amount of time on antibiotics needed to resolve an infection varies from child to child, but in general is 4 to 6 weeks for a bone infection and 3 to 4 weeks for joint or muscle infections.
Outcome
Most children will completely recover from deep infections after proper treatment. They are not likely to develop the same infection again. In most cases, children have no further problems and return to all of their activities. Some problems can occur in children who have serious and prolonged infections. These include blood clots, growth arrests, deformed bones, fractures through bone that is weakened from infection, bone death (called necrosis), and joint stiffness. However, these problems are rare.
